Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is a severe health condition that can often go unnoticed until it’s too late. This article aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of DVT, highlighting its symptoms, causes, prevention strategies, and treatment options.
What Is Deep Vein Thrombosis?
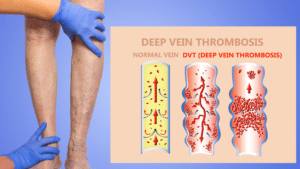
Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) is a medical condition characterized by the formation of a blood clot (thrombus) in one of your body’s deep veins, typically in the legs. The condition can lead to serious complications if the clot breaks off and travels to the lungs, causing a potentially fatal condition known as a pulmonary embolism (PE).
Recognizing the Symptoms of DVT
Symptoms of DVT may vary from person to person and can sometimes be non-existent, making it a difficult condition to detect. Common symptoms may include:
- Swelling in the affected leg, often accompanied by pain or tenderness
- Red or discolored skin on the leg
- A feeling of warmth in the affected area
However, some individuals with DVT may not exhibit any symptoms until a complication such as a pulmonary embolism occurs.
The Underlying Causes of DVT
Several factors may increase the risk of developing DVT, including:
- Prolonged periods of immobility, such as long-haul travel or bed rest
- Certain medical conditions like heart disease or inherited blood clotting disorders
- Surgery, particularly procedures involving the legs or abdomen
- Pregnancy and the postpartum period
- Hormone-based medicines, including birth control pills or hormone replacement therapy
- Smoking
- Being overweight or obese
How To Prevent Deep Vein Thrombosis
Preventing DVT involves mitigating the risk factors. Here are some proactive steps to take:
- Maintain regular physical activity: Regular exercise helps stimulate blood circulation, reducing the risk of clots.
- Stay hydrated: Adequate hydration helps prevent blood from thickening, which can contribute to clot formation.
- Limit prolonged immobility: If travel or bed rest is unavoidable, make a point to move around as much as possible.
- Adopt a healthy lifestyle: Quit smoking, manage weight, and maintain a balanced diet.
- Follow medical advice: If you’re at high risk, your healthcare provider may recommend medications or compression stockings to prevent clots.
Diagnosing and Treating DVT
If DVT is suspected, medical professionals typically use imaging tests, like ultrasound, to detect the presence of clots. Blood tests may also be used to identify certain clotting factors.
Treatment typically involves anticoagulant medications or clot-busting drugs to prevent the clot from growing and reduce the risk of a pulmonary embolism. In some severe cases, a surgical procedure might be required to remove the clot.
Remember, while DVT can be life-threatening, with the right knowledge, precautionary measures, and medical advice, it is preventable and treatable. Therefore, it’s crucial to be aware of the risks, symptoms, and available treatment options for deep vein thrombosis.

