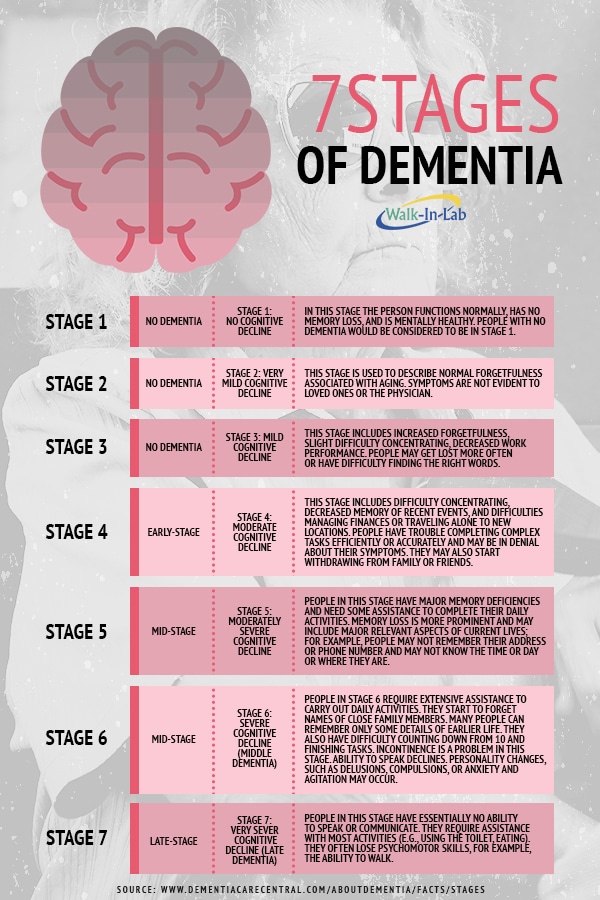
Dementia is one of the major causes of disability among older people worldwide. There is often a lack of awareness and understanding of dementia and the stages of progression. This info graphic outlines the seven stages of dementia, symptoms and conditions.
There are many other causes of dementia besides Alzheimer disease.
Occasional forgetfulness is normal and should not be a cause for concern unless it increases in frequency or interferes with daily living. However, some of the causes of cognitive decline, besides Alzheimer’s include but are not limited to:
- Medication interactions or side effects and over-medication
- Nutritional deficiencies, such as vitamin B12 deficiency
- Having a history of another condition that may contribute to mental changes, including diabetes, hypertension, or kidney, liver, or thyroid disorders
- Structural disorders like brain tumors, head injuries, and normal pressure hydrocephalus
- Degenerative diseases, including age-related cognitive decline, Huntington’s Chorea disease, Parkinson disease, and Pick disease
- Infectious diseases like HIV/AIDS, Creutzfeldt-Jakob, meningitis, encephalitis, or syphilis
- Anxiety, depression
- Heavy metal poisoning (for example, lead poisoning)
- Seizures
A range of traditional laboratory tests are used to rule out deficiencies and other diseases and conditions that could be affecting the person’s memory. This panel includes many of the tests ordered for this purpose.
A Complete Blood Count (CBC) gives important information about the numbers and kinds of cells in the blood, especially red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. A CBC helps your health professional check any symptoms, such as fatigue, weakness, or bruising, that you may have. A CBC also helps your health professional diagnose conditions, such as infection, anemia, and several other disorders. Test includes: WBC, RBC, Hemoglobin, Hematocrit, MCV, MCH, MCHC, RDW, Platelets, Neutrophils, Lymphs, Monocytes, Eos, Basos, Neutrophils (Absolute), Lymphs (Absolute), Monocytes(Absolute), Eos (Absolute), Basos (Absolute), Immature Granulocytes, Immature Grans (Abs)
Electrolytes Sodium- is important in the body’s water balance and the electrical activity of nerves and muscles and one of the major salts in body fluid. Potassium Helps to control the muscles and nerves. Chloride- Similar to sodium, chloride helps to maintain the body’s electrolyte balance. Carbon Dioxide- Total Used in detecting, evaluating, and monitoring electrolyte imbalances. Calcium- A mineral essential for development and maintenance of healthy teeth and bones. It is important also for the normal function of nerves, muscles and blood clotting.
A TSH (Thyroid Stimulating Hormone) blood test also known as the Third-generation TSH is commonly ordered to help evaluate a person’s thyroid function and aid in the diagnosis of thyroid disorders such as hyperthyroidism or hypothyroidism.
A T4 test measures the amount of a particular hormone, T4 or Thyroxine, produced by the thyroid gland. T4 helps maintain the body’s metabolism, temperature, and heart rate.
Vitamin B12 Blood Test is an important vitamin for many bodily functions, such as brain health, blood cell production, proper nerve functioning, and tissue and cellular repair.
C-Reactive Protein (CRP) Quantitative blood test determines whether a high or increasing amount of CRP in your blood suggests an acute infection or inflammation. CRP is a protein produced by the liver. Higher than normal concentrations of CRP are often an indicator of infection or inflammation in the body. This test can help determine if an infection is present but not the source of the infection. Order a CRP Blood Test online.
Sedimentation Rate (ESR) blood test Westergren – Erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) is an easy, inexpensive, nonspecific test that has been used for many years to help diagnose conditions associated with acute and chronic inflammation, including infections, cancers, and autoimmune diseases. ESR is said to be nonspecific because increases do not tell the health provider exactly where the inflammation is or what is causing it, and also because it can be affected by conditions other than inflammation. Because it is nonspecific, ESR is typically used in conjunction with other tests. ESR aids in diagnosing two specific inflammatory diseases, polymyalgia rheumatica and temporal arteritism, a high ESR being one of the main test results used to support the diagnosis. The test is also used to monitor disease activity and response to therapy in both polymyalgia rheumatica and temporal arteritism.
Get a Dementia Blood Test Panel.